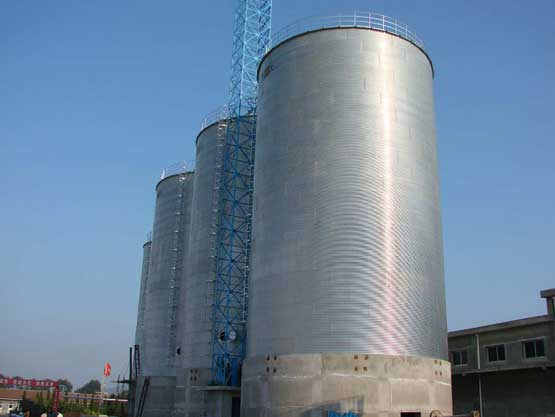
Things You Should Know About Cement Silo
Cement is a powdery water-hardening inorganic gelling material. After mixing with water in to a paste, can be hardened in the air or hardened in water better, and can put sand, stone and other materials firmly cemented together. The word “cement” comes from the Latin word “caementum”, is the meaning of gravel and rubble. In the early years the mixture of lime and volcanic ash is very similar to lime pozzolanic cement, use it to glue concrete which made of crushed stone. After hardening, the cement not only has high strength, but also can resist the erosion of fresh water or salt water. For a long time, it has been used as a kind of important cementing material, widely used in civil construction, water conservancy, national defense and other projects. Nowadays, steel silo for storing cement is widely used all around the world. It's very useful and helpful to know more about cement and cement storage silo.

Cement Classification According To Main Hydraulic Material
- Portland cement
- Aluminate cement
- Sulphoaluminate cement
- Aluminoferrite cement
- Fluoraluminate cement
- Phosphate cement
- Cement with volcanic ash or latent hydraulic material and other active material as main component.
In 2012, China's cement production reached two billion one hundred and eighty-four million tons, accounting for more than 50% of the global output. In the home decoration, the floor tiles, wall tiles paste and masonry are needed for cement. It can not only enhance the adsorption ability of the material surface, but also can protect the internal structure, at the same time can be used as a building surface leveling blanket. So in the building of each house, cement is an essential material.
Cement Storage Attention:
- Avoid damp knot hard: Wet and hard cement will reduce or even loss the original strength.
- Avoid insolation: After insolation, water in cement will quickly evaporate. Its strength will be reduced, or even completely lost.
- Avoid negative temperature and cold: When used at low temperature, cement can not be hydration, and will form crisp crack.
- Avoid high temperature and heat: Under high temperature, calcium hydroxide of cement will break down, its strength will be reduced.
- Avoid acid corrosion: Neutralization happens when acidic substances is mixed with calcium hydroxide in cement, the products is loose and expansive which is easy to be hydrolyzed after water. And it is easy to cause cement corrosion disintegration.
 Español
Español